A bone marrow transplant is a procedure to replace damaged or destroyed bone marrow with healthy bone marrow stem cells. Bone marrow is the soft, fatty tissue inside your bones. The bone marrow produces blood cells. Stem cells are immature cells in the bone marrow that give rise to all of your different blood cells.
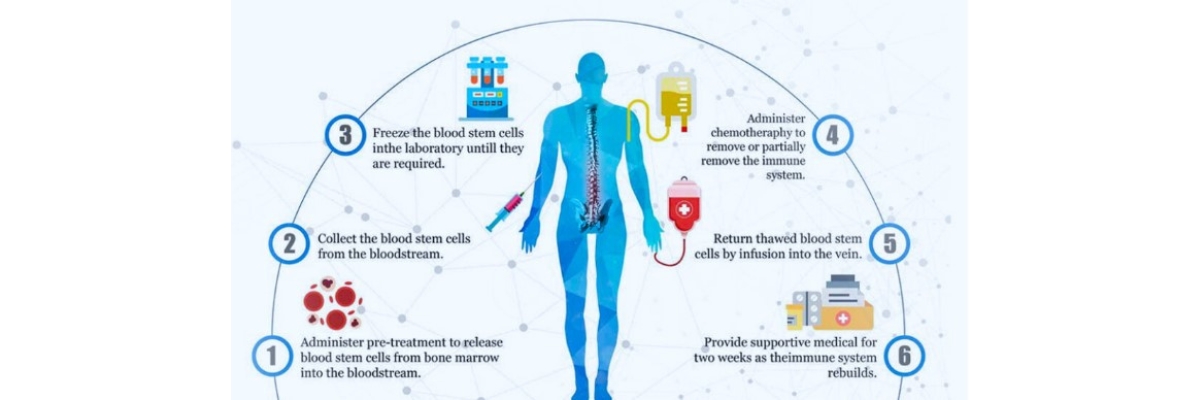
Before the transplant, Chemotherapy, Radiation, or both may be given. This may be done in 2 ways:
1. Ablative (myeloablative) treatment: High-dose chemotherapy, radiation, or both are given to kill any cancer cells. This also kills all healthy bone marrow that remains, and allows new stem cells to grow in the bone marrow.
2. Reduced intensity treatment, also called a mini transplant: People receive lower doses of chemotherapy and radiation before a transplant. This allows older people, and those with other health problems to have a transplant.
A stem cell transplant is usually done after chemotherapy and radiation is complete. The stem cells are delivered into your bloodstream usually through a tube called a central venous catheter. The process is similar to getting a blood transfusion. The stem cells travel through the blood into the bone marrow. Most times, no surgery is needed.
Donor stem cells can be collected in 2 ways:
Why the procedure id performed?
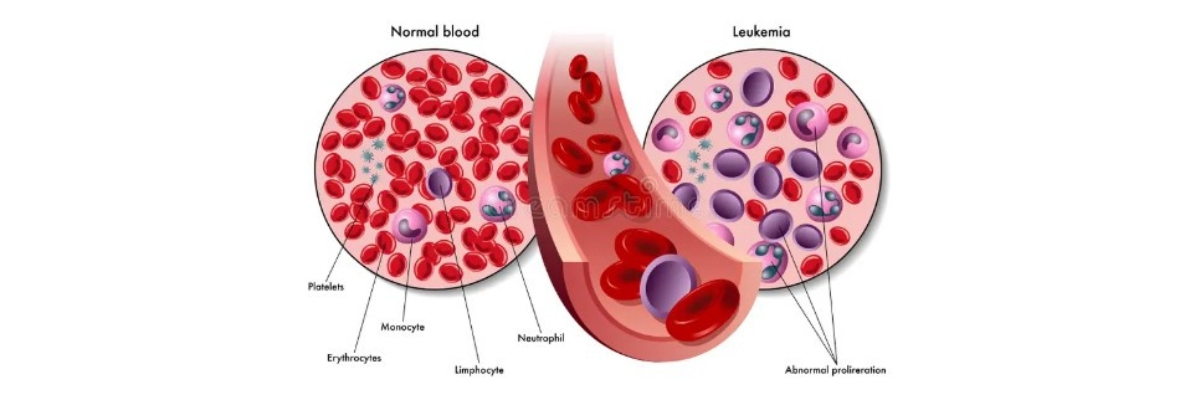
A bone marrow transplant replaces bone marrow that is either not working properly or has been destroyed (ablated) by chemotherapy or radiation. Doctors believe that for many cancers, the donor’s white blood cells may attack any remaining cancer cells, similar to when white cells attack bacteria or viruses when fighting an infection. Your doctor may recommend a bone marrow transplant if you have:
Risks
Possible complications of a bone marrow transplant depend on many things, including:
Complications may include:
Before the procedure
Your health care provider will ask about your medical history and do a physical exam. You will have many tests before treatment begins.
Before transplant, you will have 1 or 2 tubes, called catheters, inserted into a blood vessel in your neck or arms. This tube allows you to receive treatments, fluids, and sometimes nutrition. It is also used to draw blood.
Your provider will likely discuss the emotional stress of having a bone marrow transplant. You may want to meet with a counselor. It is important to talk to your family and children to help them understand what to expect.
After the procedure
A bone marrow transplant is usually done in a hospital or medical center that specializes in such treatment. Most of the time, you stay in a special bone marrow transplant unit in the center. This is to limit your chance of getting an infection.
Depending on the treatment and where it is done, all or part of an autologous or allogeneic transplant may be done as an outpatient. This means you do not have to stay in the hospital overnight.
WhatsApp us