What is Nephrology?
Nephrology is the branch of medicine that focuses on diagnosing and treating kidney-related diseases and disorders.
Why is Kidney Health Important?
The kidneys play a vital role in filtering waste, balancing fluids, and regulating blood pressure. Early detection and management can prevent serious complications.
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
Acute Kidney Injury (AKI)
Kidney Stones
Hypertension (High Blood Pressure) & Kidney Disease
Diabetic Kidney Disease
Polycystic Kidney Disease (PKD)
End-Stage Renal Disease (ESRD)
Glomerulonephritis & Nephrotic Syndrome
Kidney Function Tests & Diagnostics (Blood & Urine Tests, Imaging)
Dialysis (Hemodialysis & Peritoneal Dialysis)
Kidney Transplantation (Pre & Post Transplant Care)
Hypertension & Diabetes Management for Kidney Health
Minimally Invasive Procedures for Kidney Stones
Diet & Lifestyle Guidance for Kidney Disease Prevention
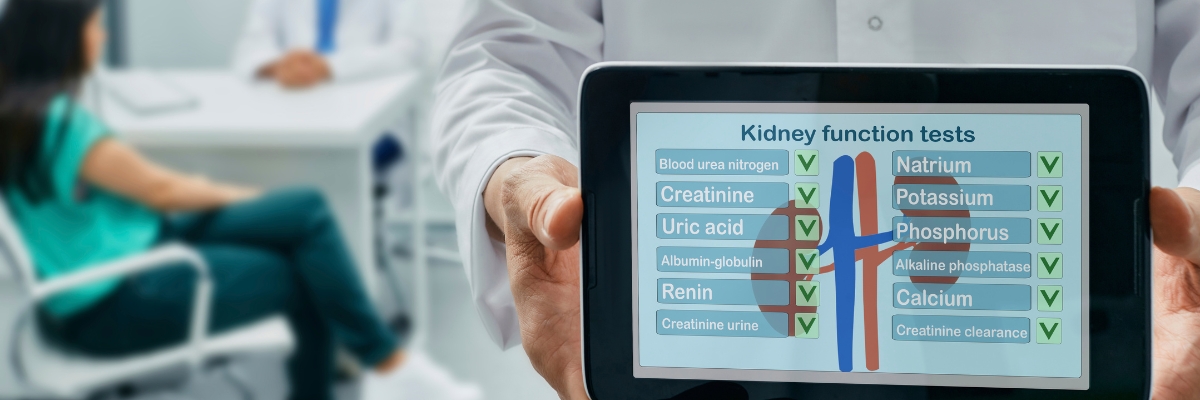
Proper kidney function is essential for filtering waste, balancing fluids, and regulating blood pressure. Kidney function tests help assess how well your kidneys are working and detect any underlying issues early. Our advanced diagnostics ensure accurate results for timely treatment and management.
These tests measure waste levels and key markers in the blood to evaluate kidney health.
Serum Creatinine Test – Measures creatinine levels, which indicate kidney filtration efficiency.
Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN) Test – Checks urea nitrogen levels, a byproduct of protein metabolism.
Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR) – Determines kidney function and disease progression.
Electrolyte Panel – Assesses sodium, potassium, and other minerals regulated by the kidneys.
Urine analysis helps detect abnormalities in kidney function, infection, or other issues.
Urinalysis (UA) – Examines urine color, pH, protein, glucose, and red/white blood cells.
Albumin-to-Creatinine Ratio (ACR) – Identifies protein leakage, an early sign of kidney disease.
24-Hour Urine Test – Measures substances filtered by the kidneys over a full day.
Advanced imaging helps visualize kidney structure and detect stones, cysts, or abnormalities.
Ultrasound – Uses sound waves to detect kidney size, blockages, or fluid retention.
CT Scan (Computed Tomography) – Provides detailed cross-sectional images to diagnose kidney disease.
MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) – Produces high-resolution images for complex kidney disorders.
Renal Biopsy – A small tissue sample is taken to diagnose kidney disease at a microscopic level.
Detects kidney disease at an early stage for better treatment outcomes.
Helps monitor chronic conditions like diabetes & hypertension that impact kidney health.
Prevents complications by ensuring proper kidney function and overall well-being.
When the kidneys can no longer function properly, dialysis becomes essential to filter waste, excess fluids, and toxins from the blood. Dialysis helps maintain a healthy balance of minerals and fluids, improving the quality of life for patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) or kidney failure.
Hemodialysis is a procedure where a machine acts as an artificial kidney to filter waste and remove excess fluids from the blood.
How It Works?
Blood is drawn from the body through a vascular access (fistula, graft, or catheter).
It passes through a dialyzer (artificial kidney), which removes toxins and extra fluids.
The filtered blood is then returned to the body.
Who Needs Hemodialysis?
Patients with end-stage renal disease (ESRD).
Individuals with severe kidney function decline who need regular blood purification.
Hemodialysis Benefits
✔ Efficient removal of toxins and waste.
✔ Performed in a hospital or dialysis center with expert supervision.
✔ Usually done 3 times a week, each session lasting 3-5 hours.
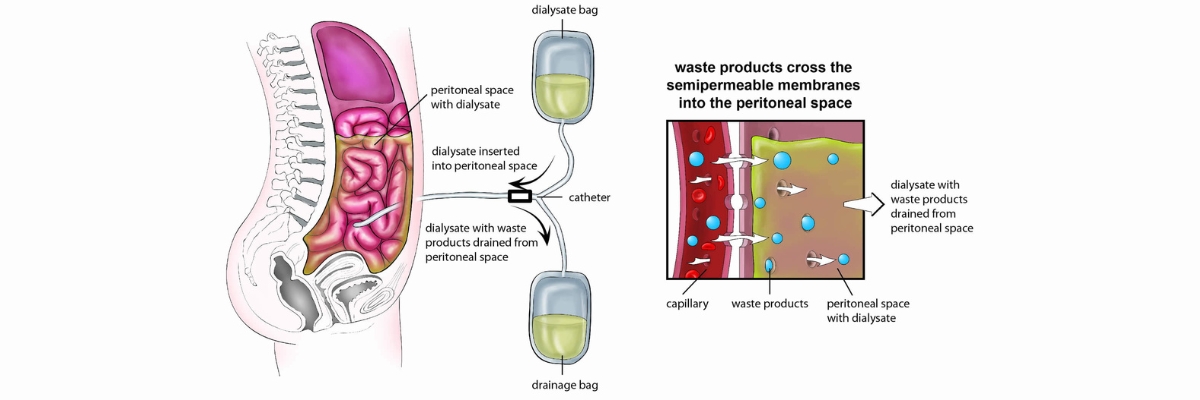
Peritoneal dialysis is a home-based treatment that uses the body’s peritoneal membrane as a natural filter.
How It Works?
A catheter is inserted into the abdomen to allow dialysis fluid (dialysate) to enter.
The dialysate absorbs waste and excess fluids from blood vessels in the peritoneal cavity.
After a few hours, the used fluid is drained and replaced with fresh dialysate.
Types of Peritoneal Dialysis
Continuous Ambulatory Peritoneal Dialysis (CAPD) – Manual exchange of fluids 3-5 times daily.
Automated Peritoneal Dialysis (APD) – A machine automates exchanges during nighttime sleep.
Peritoneal Dialysis Benefits
✔ Performed at home, offering more freedom and flexibility.
✔ Gentler on the body than hemodialysis.
✔ No need for needles or vascular access.
🔹 Severe chronic kidney disease (CKD Stage 5) or kidney failure.
🔹 High levels of creatinine, urea, and toxins in the blood.
🔹 Symptoms like swelling, nausea, fatigue, and difficulty breathing.
A kidney transplant is a life-saving procedure that replaces a failing kidney with a healthy donor kidney, restoring normal function and improving quality of life. Our expert team provides comprehensive pre- and post-transplant care to ensure a smooth and successful recovery.
A kidney transplant is the best treatment option for patients with end-stage renal disease (ESRD) or severe chronic kidney disease (CKD Stage 5). Instead of relying on dialysis, a healthy kidney from a living or deceased donor is transplanted into the patient’s body.
Benefits of Kidney Transplantation
✔ Eliminates or reduces the need for dialysis.
✔ Improves overall health and quality of life.
✔ Restores normal kidney function for better filtration and fluid balance.
✔ Enhances longevity and daily energy levels.
Before a kidney transplant, our specialists conduct a thorough evaluation to ensure the patient is a suitable candidate.
Detailed medical history & physical examination.
Blood tests & imaging to match a donor kidney.
Psychological & lifestyle assessment to determine readiness.
✔ Living Donor: A kidney from a healthy family member, friend, or altruistic donor.
✔ Deceased Donor: A kidney from an organ donor who has passed away.
Understanding the risks & benefits of transplantation.
Preparing for post-surgery care & medications.
Nutritional & lifestyle adjustments before surgery.
Performed under general anesthesia, lasting 3-4 hours.
The new kidney is placed in the lower abdomen and connected to blood vessels.
The damaged kidneys are usually left in place unless necessary to remove.
The new kidney starts functioning immediately or may take a few days.
After a successful transplant, proper care is crucial for long-term health.
Hospital Stay: 5-7 days for close monitoring.
Medications: Lifelong immunosuppressants to prevent rejection.
Hydration & Diet: Proper fluid intake and balanced nutrition.
🔹 Frequent blood tests & check-ups to track kidney function.
🔹 Monitoring for signs of organ rejection (fever, swelling, reduced urine output).
🔹 Adjusting medications to prevent infection & complications.
🔹 Healthy diet: Low salt, balanced protein, and kidney-friendly foods.
🔹 Regular exercise to maintain heart health and weight.
🔹 Avoid smoking & alcohol to protect the new kidney.
🔹 Stress management & mental well-being support.
✔ Patients with End-Stage Renal Disease (ESRD).
✔ Individuals on long-term dialysis.
✔ Severe Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD Stage 5).
✔ Genetic conditions like Polycystic Kidney Disease (PKD).
✔ Expert Nephrologists & Transplant Surgeons with years of experience.
✔ Advanced transplant facilities for safe & successful procedures.
✔ Personalized pre- & post-transplant care for best outcomes.
✔ 24/7 emergency support and dedicated patient care team.
Hypertension (High Blood Pressure) and Diabetes are the two leading causes of chronic kidney disease (CKD) and kidney failure. Proper management of these conditions is essential to protect kidney function and prevent complications. Our specialized kidney health program focuses on early detection, lifestyle modifications, and medical interventions to maintain optimal kidney health.
Hypertension & Kidneys:
High blood pressure damages the small blood vessels in the kidneys, reducing their ability to filter waste properly. This can lead to chronic kidney disease (CKD), kidney failure, or dialysis dependency.
Diabetes & Kidneys:
Uncontrolled blood sugar levels cause damage to the kidneys’ filtering units (nephrons), leading to diabetic nephropathy, a major cause of kidney failure. Early management can prevent or slow kidney disease progression.
Uncontrolled Hypertension & Diabetes Can Lead To:
🔹 Kidney failure requiring dialysis or transplant.
🔹 Increased risk of heart disease & stroke.
🔹 Fluid retention causing swelling & high blood pressure.
✔ Blood Pressure Check-ups: Maintaining BP below 130/80 mmHg is crucial.
✔ Blood Sugar Control: Monitoring HbA1c levels to keep diabetes in check.
✔ Kidney Function Tests: Routine creatinine, GFR & urine tests for early kidney damage detection.
✔ Medications:
Anti-hypertensive drugs (ACE inhibitors & ARBs) protect kidney function.
Blood sugar control medications & insulin therapy for diabetes management.
✔ Customized Diet Plan: Low sodium, sugar, and processed foods to support kidney health.
✔ Lifestyle Modifications: Weight management, regular exercise, and stress reduction techniques.
Healthy Diet for Kidney Protection
Reduce salt & sugar intake to lower blood pressure and control diabetes.
Increase fiber, lean proteins, and fresh fruits & vegetables.
Limit processed & fried foods to avoid kidney strain.
Exercise & Weight Management
At least 30 minutes of physical activity daily.
Maintain a healthy weight to prevent hypertension & diabetes complications.
Smoking & Alcohol Reduction
Quit smoking to improve circulation & kidney health.
Limit alcohol to reduce blood sugar spikes & BP fluctuations.
✔ Expert Nephrologists & Endocrinologists for personalized treatment.
✔ Comprehensive kidney health screenings & diagnostics.
✔ Tailored diet & lifestyle guidance for long-term kidney protection.
✔ Advanced treatment options for high-risk patients.
WhatsApp us